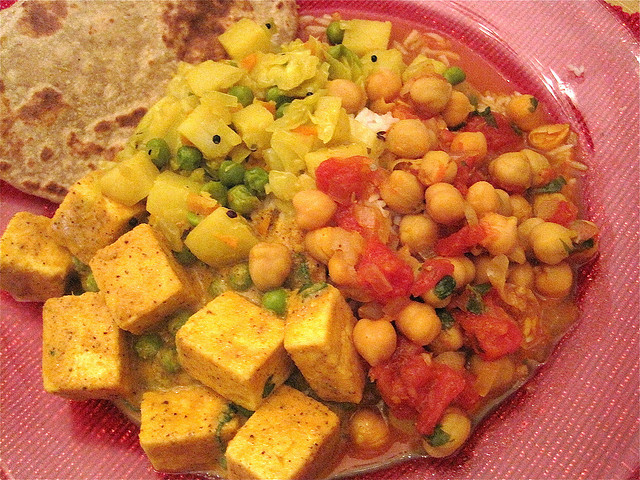
Vegan and vegetarian foods are often overlooked in muscle-building conversations, but they offer a wealth of nutrients that support metabolism and lean muscle growth. High in complex carbohydrates, fiber, and amino acids, these foods fuel workouts, enhance recovery, and keep the body’s metabolism humming efficiently.
Contrary to common belief, vegan foods aren’t just for vegans. Many athletes and fitness enthusiasts incorporate plant-based meals into their diet for a variety of reasons, including reducing bloating, managing hormones, religious and cultural traditions, and ethical concerns.
With over seventeen years of training individuals across different dietary backgrounds, I’ve seen firsthand that a well-balanced plant-based approach can fuel performance just as effectively as animal protein. In fact, with the right selection of foods, vegan diets can be powerful tools for boosting metabolism and optimizing body composition.

Metabolism is the body’s process of converting food into energy. The more muscle mass you have, the more efficiently your body burns calories—even at rest. Thus, the key to maintaining a high metabolic rate is not just cardio but also lean muscle growth.
Muscle-building requires adequate protein, amino acids, and energy-dense foods. Plant-based foods high in complex carbs, fiber, and protein are particularly effective at fueling metabolism while supporting sustained energy release.
Below are some of the best international vegetarian and vegan foods that enhance metabolism and promote lean muscle growth.
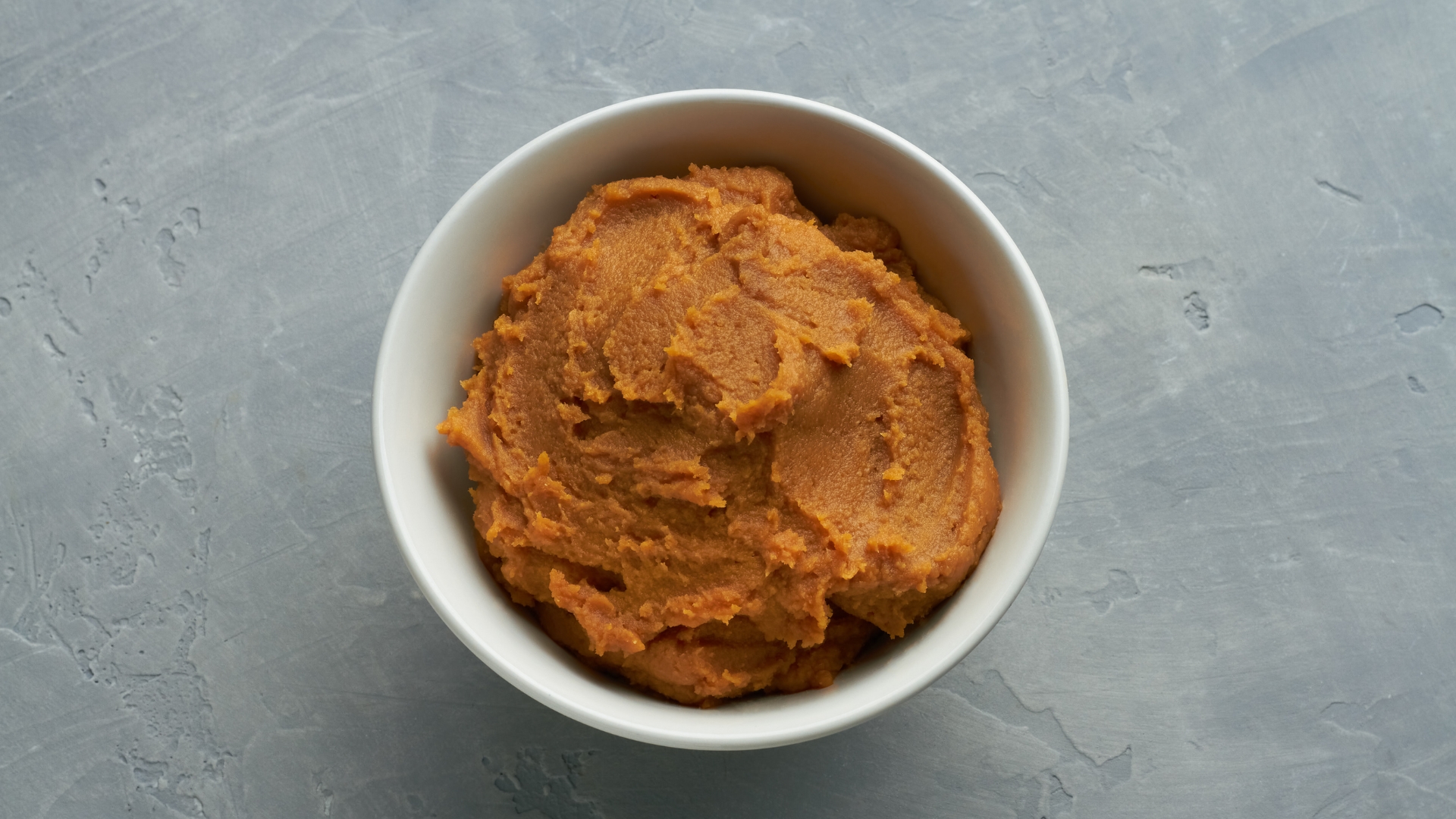

Miso is one of Japan’s most famous fermented foods, packed with umami flavor and nutritional benefits. Made from soybeans fermented with salt and koji (a type of fungus), this thick paste is a staple in Japanese cuisine, especially in miso soup. Beyond its distinctive taste, miso is rich in probiotics, which support gut health, immune function, and digestion. The fermentation process breaks down nutrients, making them more bioavailable and easier for the body to absorb. This means that miso not only provides essential amino acids and complex carbohydrates but also promotes better nutrient absorption from other foods eaten alongside it.
For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, miso offers a powerful metabolism boost. The combination of probiotics and amino acids helps improve digestion and optimize energy use during workouts. Since a healthy gut is crucial for breaking down and utilizing macronutrients efficiently, regularly incorporating miso into meals can lead to better recovery, increased endurance, and enhanced muscle-building capacity. Additionally, miso contains B vitamins, which play a vital role in energy metabolism, making it a great addition to an active lifestyle.
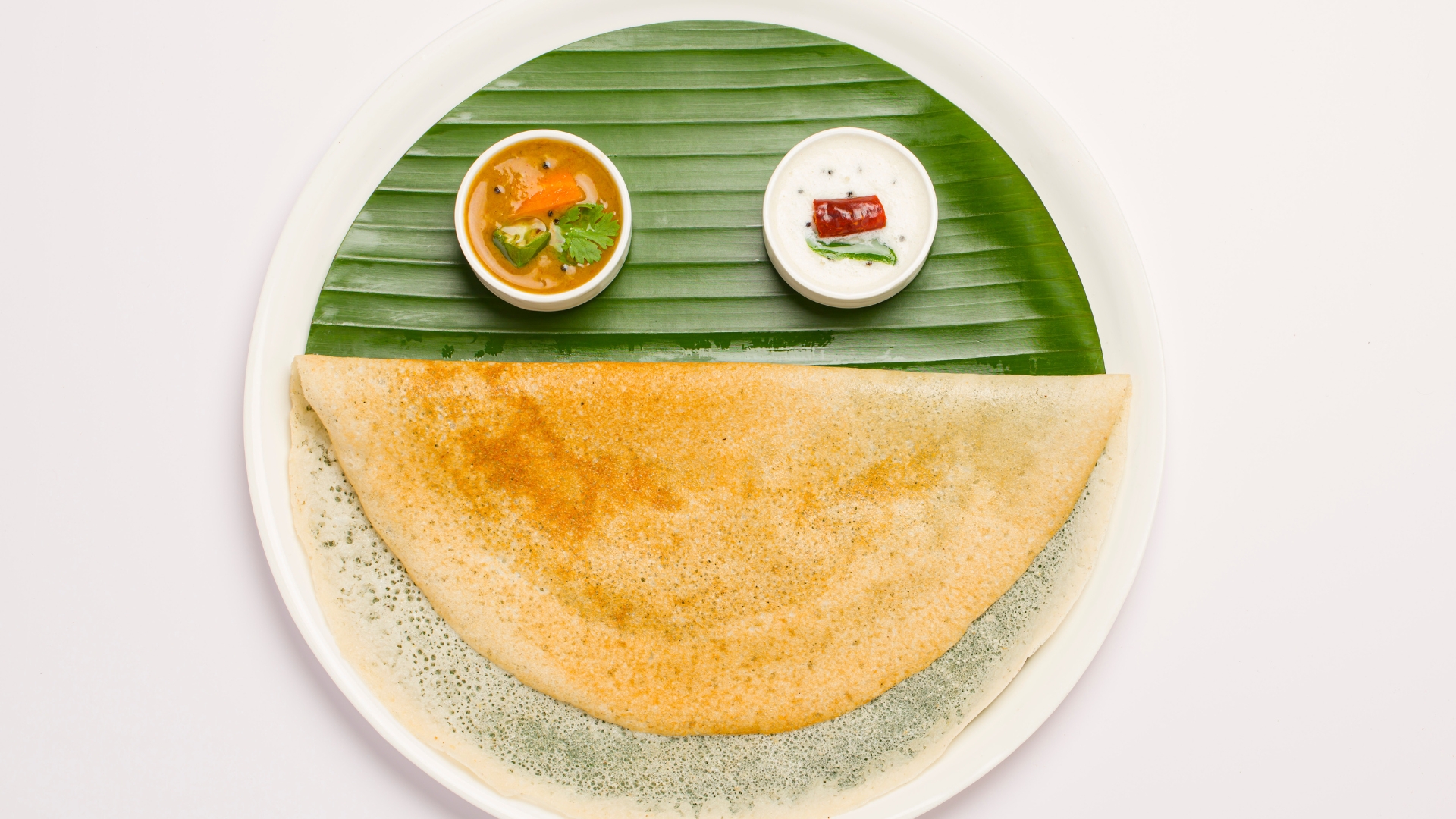

Dosa, a South Indian specialty, is a thin, crispy crepe made from a fermented batter of black lentils and rice. Light yet filling, dosa is an ideal food for those looking to boost their metabolism without consuming excessive calories. The fermentation process enhances the digestibility of lentils and rice, making nutrients like B vitamins more accessible for energy metabolism. Dosas are typically served with chutneys and sambar (a lentil-based vegetable stew), further enriching their nutritional profile. The combination of slow-digesting carbohydrates, fiber, and plant-based protein makes dosa an excellent choice for sustained energy and muscle recovery.
One of the key benefits of dosa is its high content of complex carbohydrates, which provide long-lasting energy—perfect for those engaged in endurance training or high-intensity workouts. Unlike processed carbs, dosa’s whole-grain base keeps blood sugar levels stable, preventing energy crashes. Additionally, its fiber content supports gut health, which is directly linked to improved metabolism. When combined with nutrient-dense sides like coconut chutney or vegetable sambar, dosa becomes a well-rounded meal that fuels muscle growth and overall performance.
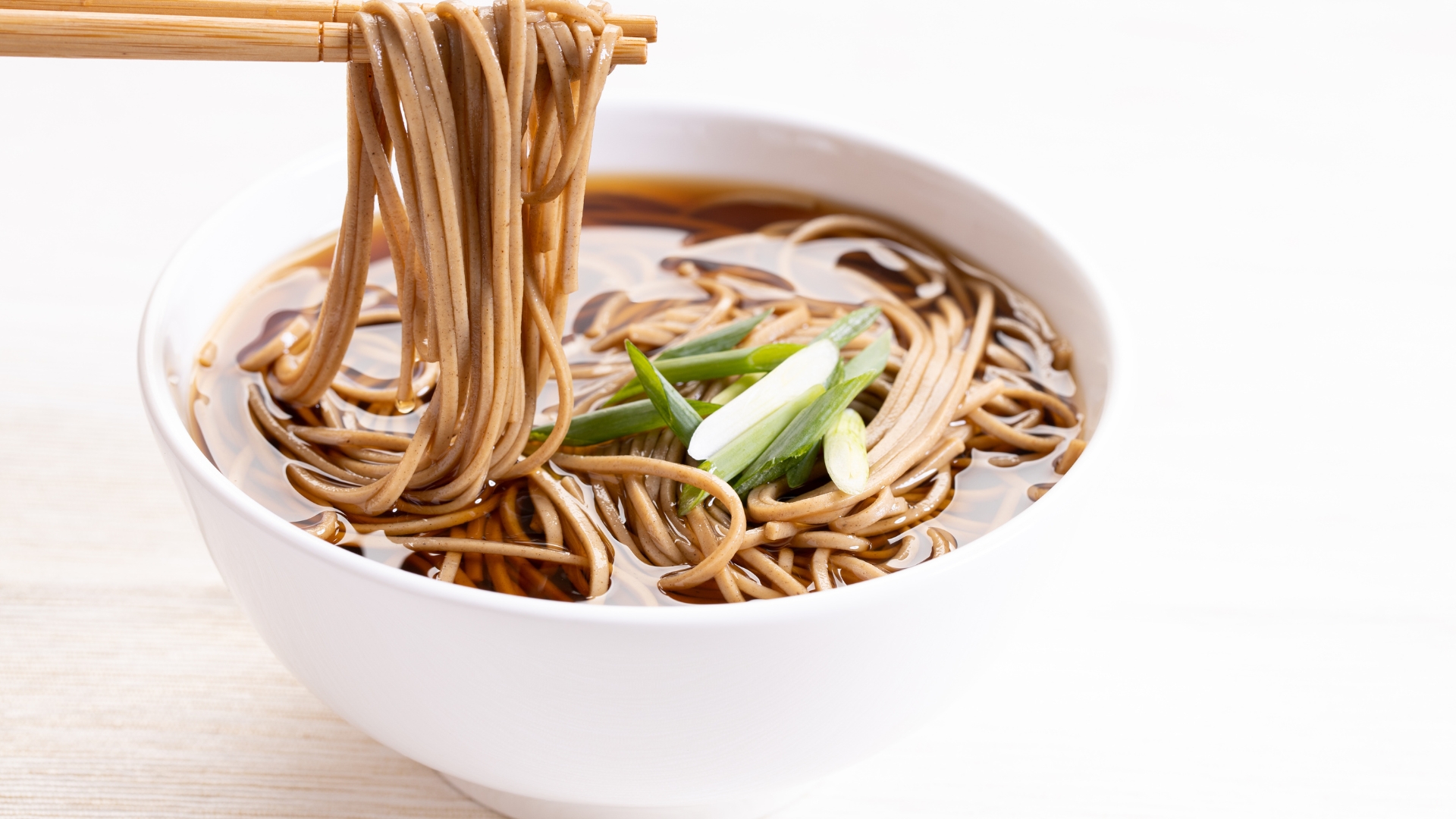

Soba noodles, made primarily from buckwheat, are a nutritious alternative to traditional wheat-based noodles. Buckwheat is naturally gluten-free and contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete protein source—something rare in plant-based foods. Soba’s high fiber content slows digestion, providing a steady release of energy and preventing blood sugar spikes. Additionally, buckwheat is rich in rutin, an antioxidant that supports circulation and reduces inflammation, both of which are beneficial for recovery and muscle repair.
For those focused on building lean muscle and improving endurance, soba noodles offer a perfect balance of protein, complex carbohydrates, and micronutrients. The presence of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) makes soba particularly effective for muscle recovery, as these amino acids help reduce muscle soreness and accelerate tissue repair. Whether served cold with a light soy-based sauce or in a warm broth with vegetables, soba provides a filling yet easily digestible meal that supports metabolism and athletic performance.
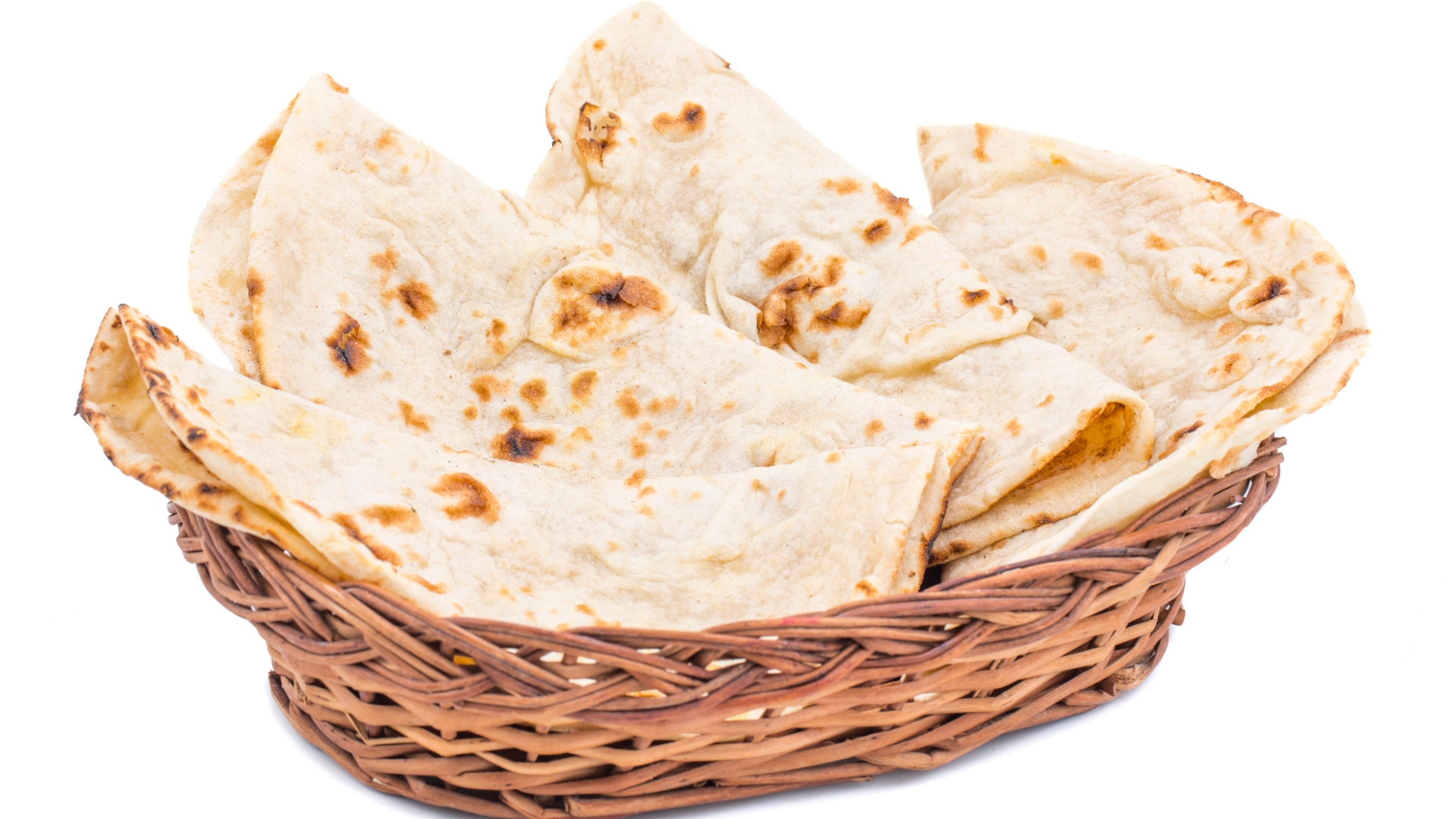

Roti and pita are two staple flatbreads found in cuisines across the world, from India to the Mediterranean. While roti is an unleavened whole wheat flatbread, pita is a leavened bread that forms an inner pocket when baked. Both are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates, which provide sustained energy throughout the day. Roti, often made with whole wheat or millet flour, is a fiber-rich option that supports digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Pita, on the other hand, is slightly fluffier and provides a good balance of carbohydrates and protein, making it a solid choice for those looking to refuel after a workout.
For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, roti and pita can serve as an ideal post-workout carbohydrate source, replenishing glycogen stores and preventing muscle fatigue. When paired with protein-rich foods like hummus, lentils, or grilled vegetables, these breads become a powerhouse meal that supports both muscle recovery and metabolic efficiency. Additionally, roti contains monounsaturated fats, which are beneficial for anaerobic workouts that require quick bursts of energy, such as sprinting or weightlifting. Whether eaten with a nutrient-dense spread or used as a wrap for lean proteins, these flatbreads offer a balanced and satisfying energy source.
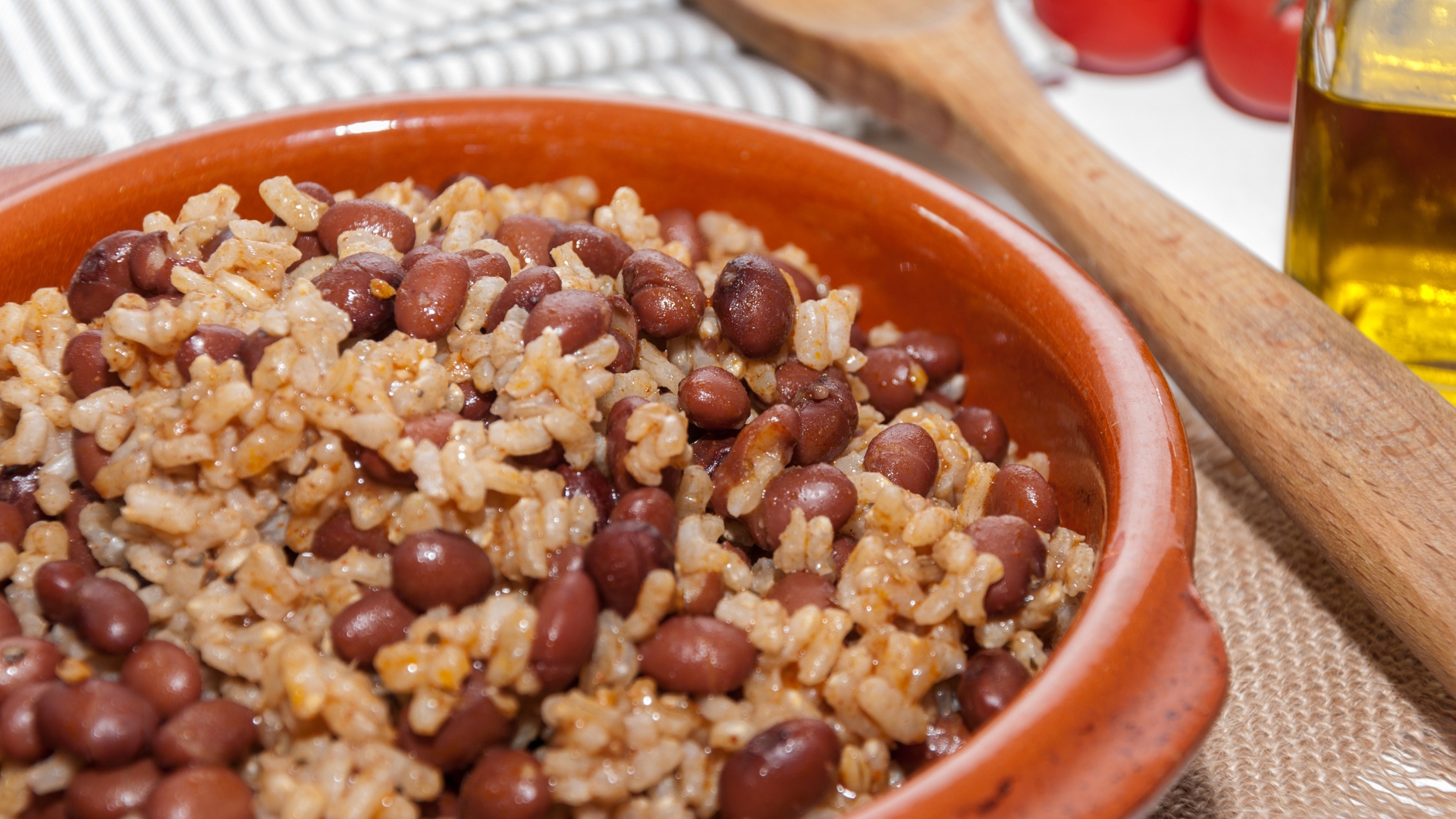

Red beans and rice is a classic dish found in various cultures, particularly in the Caribbean, Latin America, and the Southern United States. This simple yet nutrient-dense meal is built around red kidney beans, which are one of the best sources of plant-based protein, fiber, and essential minerals. Beans provide slow-digesting carbohydrates that help sustain energy levels throughout the day, while the fiber supports digestive health and helps regulate metabolism. Rice, typically white or brown, acts as a complementary protein source, making this dish a complete protein meal with all nine essential amino acids.
For those engaged in endurance training or muscle-building routines, red beans and rice offer a winning combination of energy-boosting carbohydrates, protein for muscle recovery, and iron for oxygen transport. Iron plays a critical role in maintaining stamina and endurance, as it helps red blood cells carry oxygen to working muscles. The antioxidant content in red beans also helps reduce inflammation and promote faster recovery after intense workouts. With its balance of macronutrients and affordability, this meal is a staple for athletes looking to build strength and maintain a high-functioning metabolism.
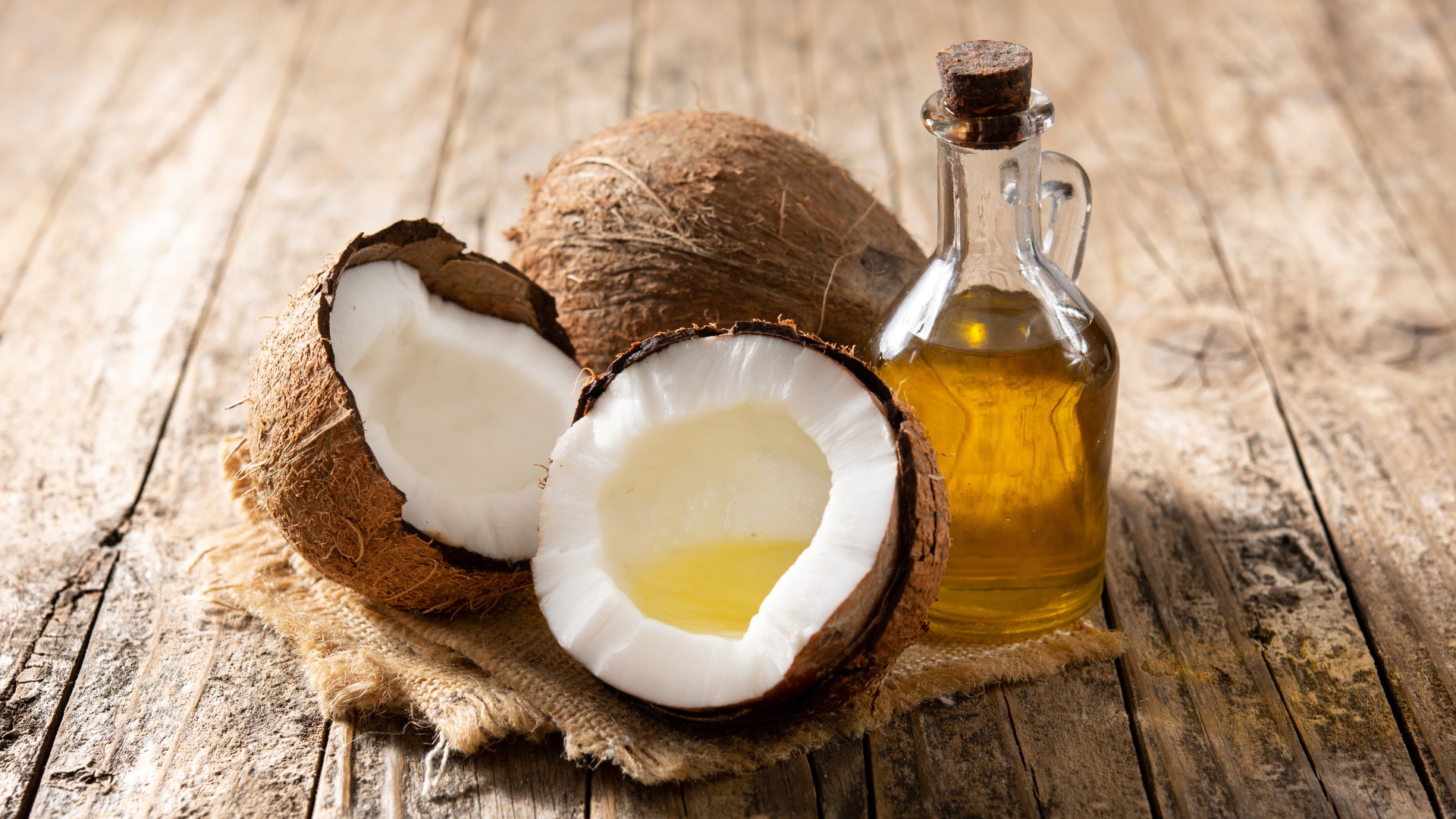

Coconut oil has gained massive popularity in the fitness and nutrition space due to its unique medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), a type of fat that is metabolized differently from traditional long-chain fats. Unlike most dietary fats, MCTs are quickly absorbed by the liver and converted into immediate energy, making coconut oil an excellent pre-workout fuel for high-intensity activities. This makes it particularly useful for endurance athletes, fighters, and strength trainers who need a rapid and sustained energy source.
While coconut oil has many benefits for energy production and fat oxidation, it is not ideal for those strictly focused on weight loss, as it is still a calorie-dense fat. However, for athletes with high energy demands, adding coconut oil to meals or coffee can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and prolonged endurance. Studies also suggest that MCTs may increase thermogenesis (calorie burning) and enhance fat metabolism, which can be beneficial when consumed in moderation. Whether used for cooking, blended into smoothies, or added to pre-workout drinks, coconut oil is a powerful tool for those looking to optimize metabolism and improve exercise performance.
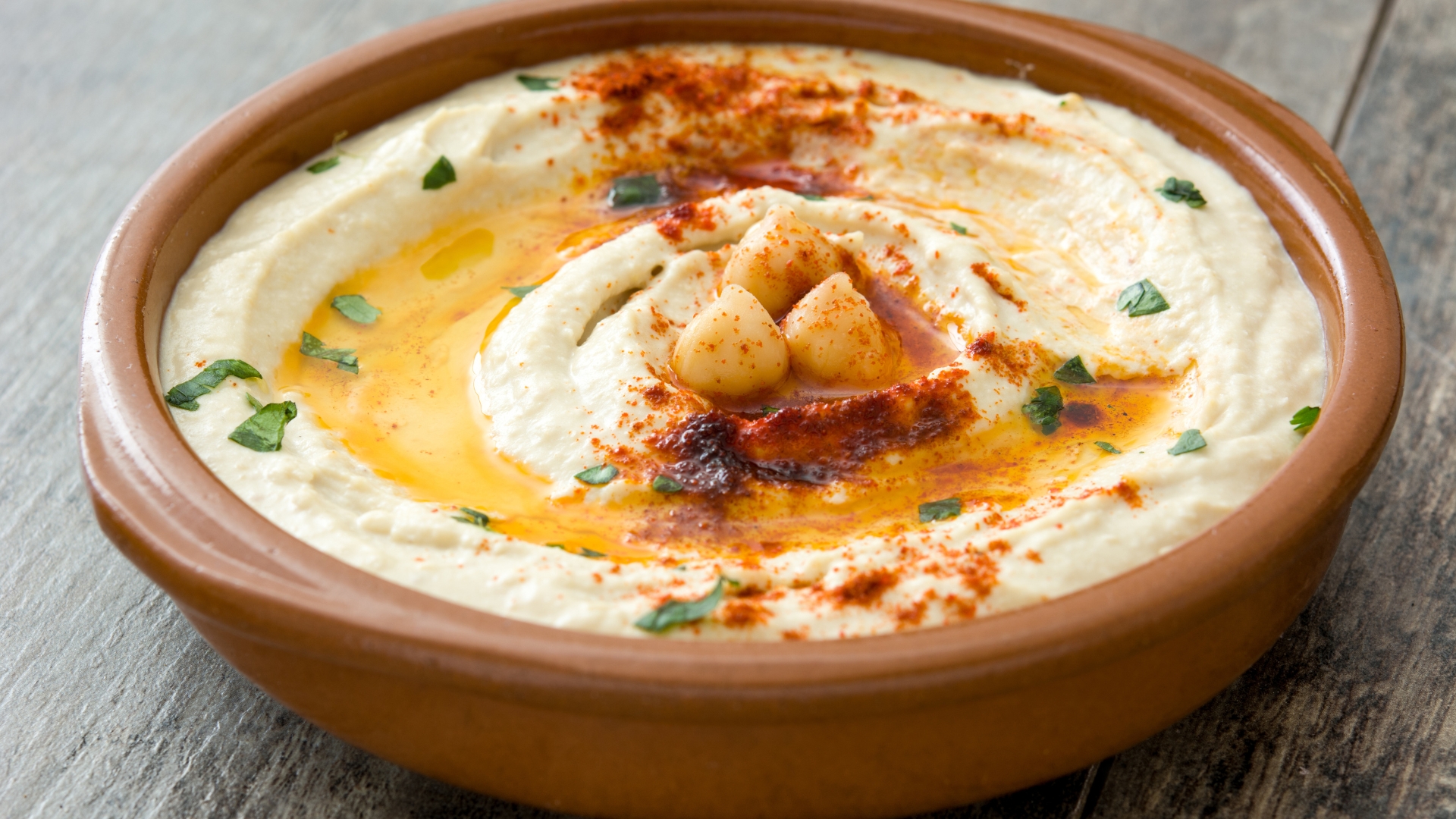

Hummus is a staple dish in Middle Eastern and Mediterranean cuisine, made primarily from blended chickpeas, olive oil, tahini, lemon juice, and spices. This nutrient-dense dip is packed with plant-based protein, fiber, and healthy fats, making it an excellent choice for both muscle-building and metabolic support. The combination of protein and fiber helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, while the monounsaturated fats from olive oil improve insulin sensitivity and fat metabolism. Hummus is also high in essential minerals like iron, magnesium, and folate, which contribute to energy production and muscle recovery.
For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, hummus serves as a versatile recovery food that supports lean muscle growth and satiety. Whether spread on whole-grain pita, paired with fresh vegetables, or used as a protein-rich sandwich filling, it helps fuel post-workout recovery while preventing overconsumption of processed foods. Thanks to its high fiber content, hummus promotes digestive health and helps regulate metabolism, making it a valuable addition to any performance-focused diet.
Protein powder is one of the most convenient and efficient ways to meet daily protein intake requirements, particularly for athletes, bodybuilders, and individuals on a plant-based diet. High-quality vegan protein powders contain a blend of plant-based sources like hemp, rice, pea, and soy, ensuring a complete amino acid profile necessary for muscle recovery and metabolism. Unlike whole food sources, protein powders offer rapid absorption, making them an excellent choice post-workout to speed up muscle repair.
For individuals looking to maximize strength, endurance, and recovery, protein powder is an essential dietary tool. Since muscle mass directly influences metabolism, consuming adequate protein is crucial for maintaining lean body composition and preventing muscle loss. Many vegan protein powders also come fortified with B vitamins, digestive enzymes, and electrolytes, further enhancing nutrient absorption and overall metabolic efficiency. Whether blended into smoothies, mixed with plant-based milk, or stirred into oatmeal, protein powder offers a quick and effective way to support training and energy metabolism.
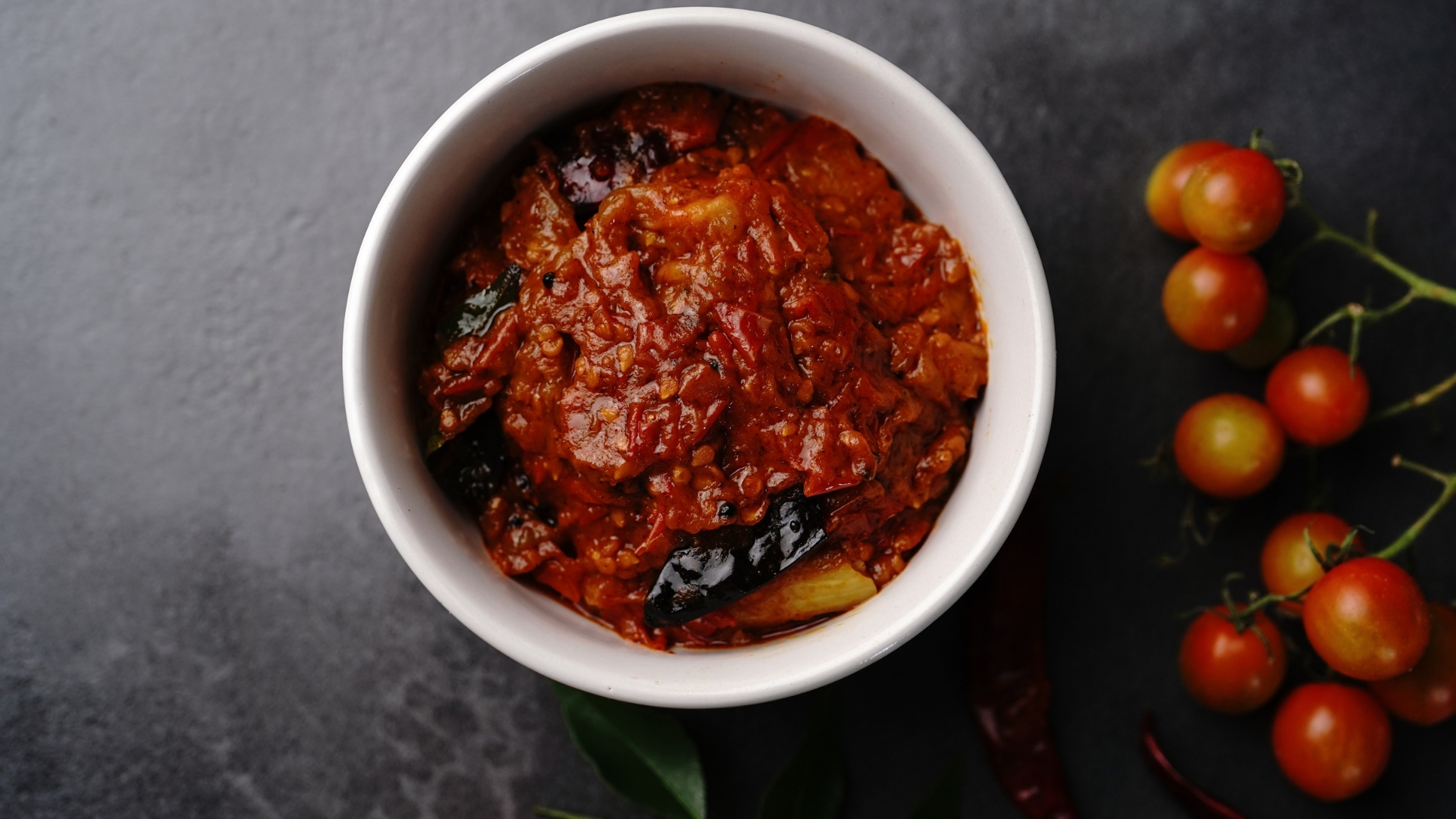

Chutney is a flavorful condiment made from a blend of fruits, vegetables, herbs, vinegar, and spices, commonly found in Indian and South Asian cuisines. These sweet, spicy, or tangy sauces add depth to meals while offering a range of health benefits. The natural sugars in fruit-based chutneys provide quick-digesting carbohydrates, making them a great pre-workout snack to fuel high-intensity exercise. Additionally, many chutneys contain anti-inflammatory ingredients like turmeric, garlic, and ginger, which aid muscle recovery and digestive health.
Incorporating chutney into meals enhances the bioavailability of key nutrients, especially when paired with complex carbohydrates and proteins. The fiber-rich nature of chutney also aids digestion and gut health, which plays a crucial role in metabolic efficiency. Whether used as a dip, marinade, or sauce, chutney can help enhance the nutrient profile of plant-based meals, making it an ideal addition to energy-boosting diets.
Eggplant is an often-underrated vegetable with impressive metabolic benefits. Known for its rich fiber content and phytonutrients, eggplant helps regulate blood sugar levels and enhance digestion, making it a fantastic choice for those aiming to improve metabolism. It is also low in calories but high in water content, making it an ideal food for those looking to manage weight while building lean muscle. Additionally, eggplant contains chlorogenic acid, a potent antioxidant that helps combat inflammation and oxidative stress, two factors that can hinder athletic performance and muscle recovery.
Eggplant is incredibly versatile, absorbing flavors well in various cooking styles, whether grilled, roasted, or mashed into dishes like baba ganoush. Because it has a moderate amount of carbohydrates along with some natural sugars, it serves as an excellent pre-workout meal that provides slow-digesting energy. Pairing eggplant with healthy fats like olive oil and tahini enhances its nutrient absorption, making it a powerhouse food for athletes and active individuals.
Food | Protein (per serving) | Metabolism Benefits | Best Time to Eat |
Miso | 5g | Gut health, digestion, post-workout recovery | Lunch or post-workout |
Dosa | 8g | High in B vitamins, aids glycogen replenishment | Breakfast or pre-workout |
Soba (Buckwheat) | 12g | Complete amino acid profile, high fiber | Lunch or dinner |
Roti/Pita | 10g | Complex carbs for sustained energy, supports endurance | Pre-workout or post-workout |
Red Beans & Rice | 15g | High in fiber, complete protein with rice, iron-rich | Post-workout recovery |
Coconut Oil | 0g | Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) for fast energy | Pre-workout (for endurance) |
Hummus | 7g | Monounsaturated fats, fiber-rich for metabolism | Snack or post-workout |
Protein Powder | 25g | Rapid protein absorption for muscle recovery | Post-workout |
Chutney | 3g | Quick-digesting natural sugars for energy | Pre-workout |
Eggplant | 2g | High fiber, antioxidant-rich for metabolism support | Pre-workout or lunch |
The power of international vegan and vegetarian foods goes beyond just ethical or dietary choices—they are metabolic powerhouses that fuel strength, endurance, and lean muscle growth. Whether you’re an athlete, fighter, weightlifter, or just someone looking to optimize performance, the foods outlined in this guide offer a scientifically-backed approach to sustaining energy, improving digestion, and accelerating muscle recovery.
A high-functioning metabolism isn’t just about burning calories—it’s about how efficiently your body converts food into usable energy. From Miso’s gut-supporting benefits to the quick-releasing energy of chutney and coconut oil, each food plays a critical role in supporting training adaptations, hormonal balance, and sustained endurance.
By incorporating nutrient-dense whole foods, you’re not only optimizing muscle synthesis but also reducing inflammation, supporting recovery, and preventing metabolic slowdowns. These foods, combined with a strategic training plan, hydration, and proper macronutrient balance, will set the foundation for consistent progress in fitness, strength, and longevity.
The best part? These foods are readily available, culturally rich, and flavorful—making it easier than ever to eat for both performance and pleasure. Fuel your body intelligently, consistently, and sustainably—because true strength starts with what you put on your plate.
Yes, muscle growth is possible on a vegan or vegetarian diet as long as protein intake, essential amino acids, and overall calorie consumption are adequate. Incorporating high-protein plant-based foods like lentils, beans, quinoa, and protein powders ensures sufficient muscle protein synthesis and recovery.
Some of the best vegan and vegetarian protein sources include:
Yes! Fiber-rich, complex carbohydrate foods help regulate blood sugar, sustain energy levels, and promote lean muscle retention, which is critical for an efficient metabolism. Fermented foods like miso and high-antioxidant foods like eggplant further aid in digestion and metabolic efficiency.
Before a workout, you need easily digestible carbohydrates for quick energy. Some great pre-workout plant-based options include:
Creatine is naturally found in animal products, but plant-based eaters can supplement with creatine monohydrate to improve power output, muscle endurance, and overall performance. Since vegetarians and vegans tend to have lower natural creatine levels, supplementation can provide a significant performance advantage.
A perfect post-workout meal should include protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats. Some great options include:
No, vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products, so vegans and some vegetarians should supplement with B12 or consume fortified foods like nutritional yeast, plant-based milks, and fortified cereals.
Since fish is a primary Omega-3 source, plant-based alternatives include:
Absolutely! Whole food, plant-based diets are naturally high in fiber, lower in processed fats, and loaded with micronutrients that support efficient fat metabolism. By focusing on whole grains, legumes, and lean plant proteins, you can reduce body fat while maintaining muscle mass.
coachjohanncscs.com only uses primary research and scholarly studies as references over secondary sites. Other references are primarily from reputable social media accounts of experts only in the fields of health, nutrition, sports science, physiology, psychology, and physical therapy.